Study of meiosis in onion flower bud with the help of permanent slides
Practical Notebook Biology Standard XII
Biology
Answeres
Practical Notebook
Standard XII
Class-12th
science
https://drive.google.com/file/d/10NrtEg6k0Hh8ttkenvZvI2EzFqZN8vPr/view?usp=sharing
7. Study of meiosis in onion flower bud with the help of permanent slides.
Aim:
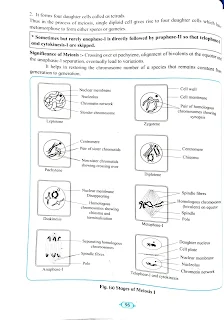
To study and identify different stages of meiosis. Principle 1 Meiosis is a special type of cell division that occurs in the diploid reproductive or germ tissue (cells). It is a reduction division that results in the formation of four haploid daughter cells each receiving half of the total number of chromosomes than those present in the mother cell from which it is produced Observation For the preparation of meiosis slides, generally, anther of Lily or Onion is used. Meiosis can be studied with the help of stained permanent slides of T. S. of the anther. Permanent slides should be observed under the high power of a compound microscope. Meiosis is a process that occurs in two steps viz. A) Meiosis-1 B) Meiosis-11
1. Melosis-1:
Is a reduction division in which chromosome number is reduced to half of the number of chromosomes present in the parent cell. It is completed into two stages- A) Karyokinesis I and B) Cytokinesis 1. A. Karyokinesis 1: It takes place in four sub-stages. 1. Prophase 1: It is an initial and very lengthy phase, further divided into five sub-stages I.
Leptotene:
Chromosomes appear like long, thin, beaded threads.
II. Zygotene:
It is characterized by paring of homologous chromosomes called 'Synopsis paired chromosomes are called bivalents or tetrad. lii. Pachytene - Each bivalent tetrad consists of four chromatids (two pairs) and each pair is united by a centromere. In this stage crossing over (X-shaped chiasmata) occurs in between two non-sister chromatids of bivalent. Exchange of genetic material or chromatid segments takes place which results in recombination that leads to variation and thus the evolution of the organism. Iv. Diplotene - After crossing over, homologous chromosomes start repelling from each other but remain attached to the chiasmata. v. Diakinesis - Terminalization i.e. shifting of chiasmata toward the end of chromatid takes place. Nucleolus and nuclear membranes are completely disorganized and disappear. 2. Metaphase 1: 1. An imaginary line (Equatorial plane) develops at the center of the cell. ii. The pair of chromosomes (bivalents) are arranged at the plane in such a way that they lie equidistant on either side of the plane, their arms towards the equator and centromere towards the pole. iii. In the end, spindle formation takes place which helps in the arrangement and movements of chromosomes. iv. Members of each bivalent are connected to only one of the two poles but opposite poles. 3. Anaphase 1: 1. chromosome number is reduced to half of the total number. It is an important stage of meiosis - 1, as reduction division takes place in this stage 1. c. toward opposite poles. ii. Tactile (spindle) fibers start condensing, become shorter and pull chromosomes (homologs).
Opposite poles.
1. It results in the separation and dragging of recombined homologous chromosomes towards 4. Telophase I: i. In this phase, chromosomes reach the opposite poles. 11. Nucleolus gets reorganized and then reappears. I Nuclear men. brane gets developed around each set of chromosomes, forming two daughter nuclei. This is how Karyokinesis - I come to an end. 20t B) Cytokinesis I: 1. It occurs by the formation of the cell plate in a plant cell, which is formed at the equator of the dividing cell.
2. Two daughter cells are formed having a single, haploid nucleus each. This is the end of meiosis - 1. At the end of meiosis - I, two daughter cells are formed which are qualitatively different from each other but are quantitatively identical. Both the cells now undergo meiosis - Il simultaneously. The interphase following meiosis - I do not involve duplication of genetic material. II. Meiosis - II: It is also divided into A) Karyokinesis II and B) Cytokinesis II A) Karyokin…








Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you to visit My blog