Study of T.S. testis, T.S. ovary and V.S. of blastula, through permanent slides
Practical Notebook Biology Standard XII
Biology
Answeres
Practical Notebook
Standard XII
Class-12th
science
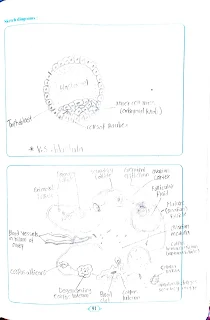
T.S. Testis: Date Internal structure of testis shows the presence of tunica albuginea and seminiferous tubules. Testis 6. Study of T. S. testis, T. S. ovary, and V. S. of blastula, through permanent slides. Is externally covered by fibrous connective tissue called tunica albuginea. It is internally covered by tunica vascularis formed by capillaries and externally by an incomplete covering called tunica vaginalis. Seminiferous tubules are lined by cuboidal germinal epithelial cells.
It shows different stages of spermatogenesis lic spermatogonia, primary and secondary spermatocytes, spermatids, and sperms. Few large pyramidal cells are present interrupting germinal epithelia are nurse cells or Sertoli cells. Sperm bundles get attached to Sertoli cells with their heads. The function of Sertoli cells is to provide nourishment to the sperms till maturation.
Fig. Sagittal section of testis showing seminiferous tubules Fig 87
2. T.S. (or L.S.) of over!
Internally the mammalian ovary shows a compact structure with an outer cortex and inner medulla. The medulla shows connective tissue called the stroma. The cortex is lined by the germinal epithelium. The cortical region shows different stages of development of ovarian follicles or griffin follicles. Each follicle contains a large ovum surrounded by many layers of follicle cells. Different stages of developing ovarian follicles are seen in the cortex and consist of oocytes in different developmental stages. In the beginning, a single layer of follicular cells around each oocyte is seon. The entire structure is called a primordial follicle. The primary follicles are surrounded first by a layer of follicular cells. As the follicle grows forms secondary and mature follicles.
The follicle grows, it forms a clean glycoprotein layer, called the zona pellucida between primary oocyte and granulosa cells. The innermost layer of granulosa cells becomes firmly attached to the zona pellucida to form corona radiata. (Corona -crown; radiate -radiating) The outermost granulosa cells rest on a basement membrane. Encircling the basement membrane is a region called theca folliculi. Many capillaries are present in the theca folliculi.
As a primary follicle continues to grow, the theca follicle gets differentiated into - i) Theca interna: - A highly vascularized internal secretory cells. Ca ii) Theca Externa: - An outer layer of connective tissue cells. One ovum from a mature follicle is released from on ovary in every menstrual cycle alternately in right and left ovary). It may also show the presence of a mass of yellow cells called corpus luteum, formed in the antrum or follicular cavity of an empty Graffian follicle after the release of its ovum (ovulation). towards the end of pregnancy. The ovarian cortex may also show a white body or corpus Albicans representing a degenerating corpus luteum if the ovum is not fertilized. Fig. T. S. of the ovary







Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you to visit My blog